Overview
- HL7 (Health Level Seven): A set of international standards for the exchange, integration, sharing, and retrieval of electronic health information.
- Trust Integration Engine (TIE): Manages the exchange of HL7 messages between different systems within a healthcare trust.
- Interweave Exchange: Facilitates interoperability between different healthcare systems, allowing seamless exchange of HL7 messages.
HL7 Messaging
Purpose: Standardizes the way healthcare information is exchanged to ensure compatibility and reduce errors.
Structure:
- Segments: HL7 messages are structured into segments (e.g., MSH, PID, OBX), each containing fields with specific information.
- MSH (Message Header): Contains information about the message itself, such as sender, receiver, and date/time of the message.
- PID (Patient Identification): Contains patient identification information like patient ID, name, and address.
- OBX (Observation/Result): Contains observation results, like lab test results.
Example HL7 Message:
In this example, the message header (MSH) indicates that this is an ADT (Admit Discharge Transfer) message, while the PID segment identifies the patient, and the OBX segment contains the lab test result for glucose.
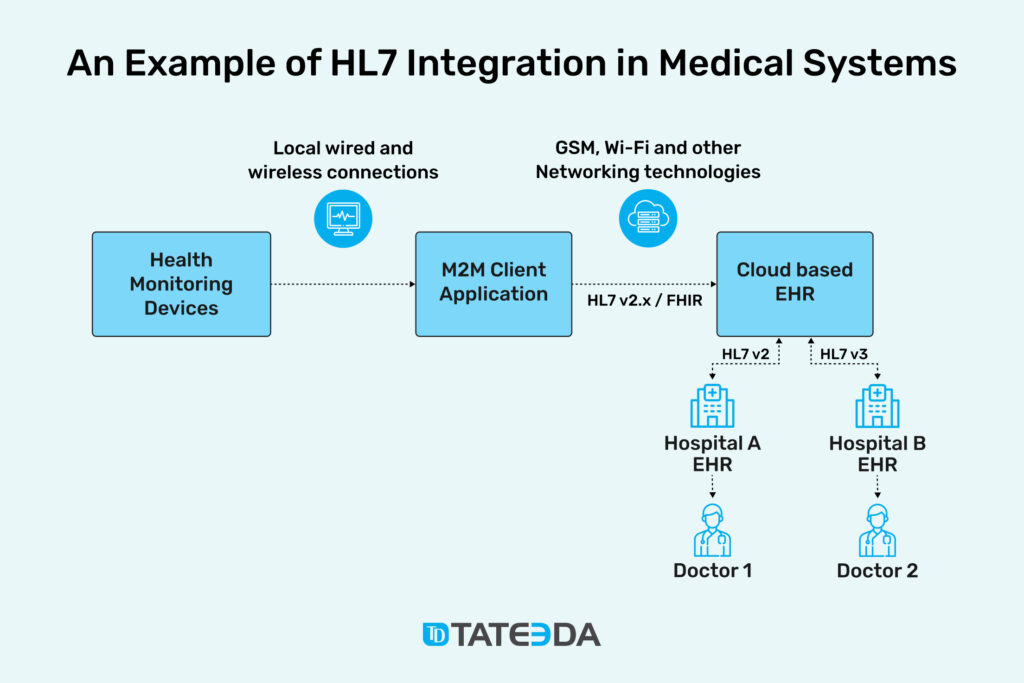
Trust Integration Engine (TIE)
Function: Acts as a middleware that routes HL7 messages between various systems within a healthcare trust.
Capabilities:
- Message Transformation: Converts HL7 messages from one format to another as needed.
- Routing: Directs messages to the appropriate systems based on predefined rules.
- Monitoring and Logging: Tracks message flow for auditing and troubleshooting.
Example Scenario: A patient’s admission details are entered into the hospital’s electronic health record (EHR) system. The TIE takes this HL7 ADT message and routes it to the lab system, notifying them of the new admission.
Image: 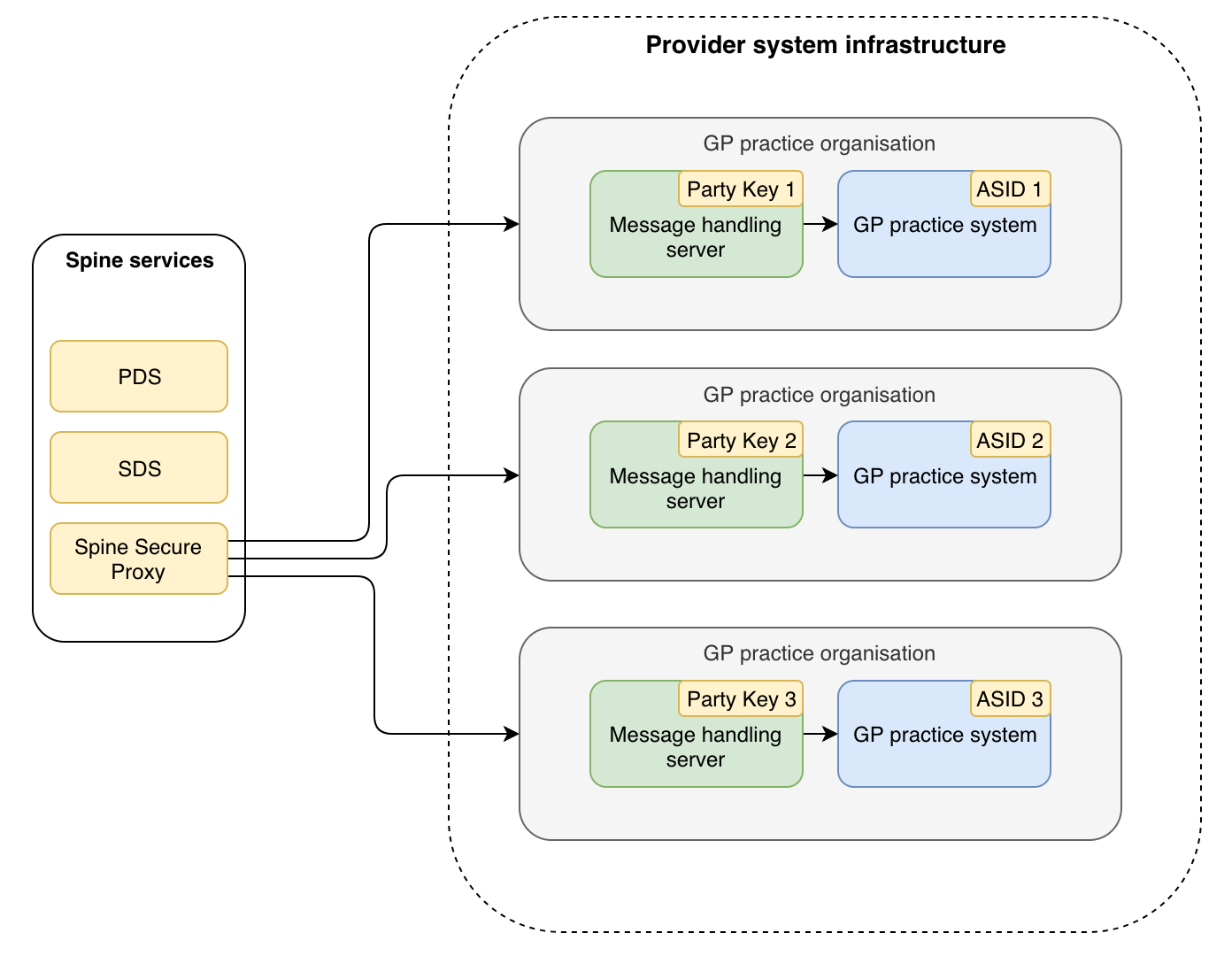
Interweave Exchange
Function: Enhances interoperability by enabling different healthcare systems to communicate effectively.
Capabilities:
- Integration: Connects disparate systems, facilitating the exchange of HL7 messages.
- Standardization: Ensures all systems adhere to HL7 standards for consistency.
- Security: Implements robust security measures to protect sensitive health information during transmission.
Example Scenario: An ambulance service records patient data during transport. Using Interweave Exchange, this data is seamlessly transmitted to the receiving hospital’s EHR system, ensuring continuity of care upon arrival.
Image: 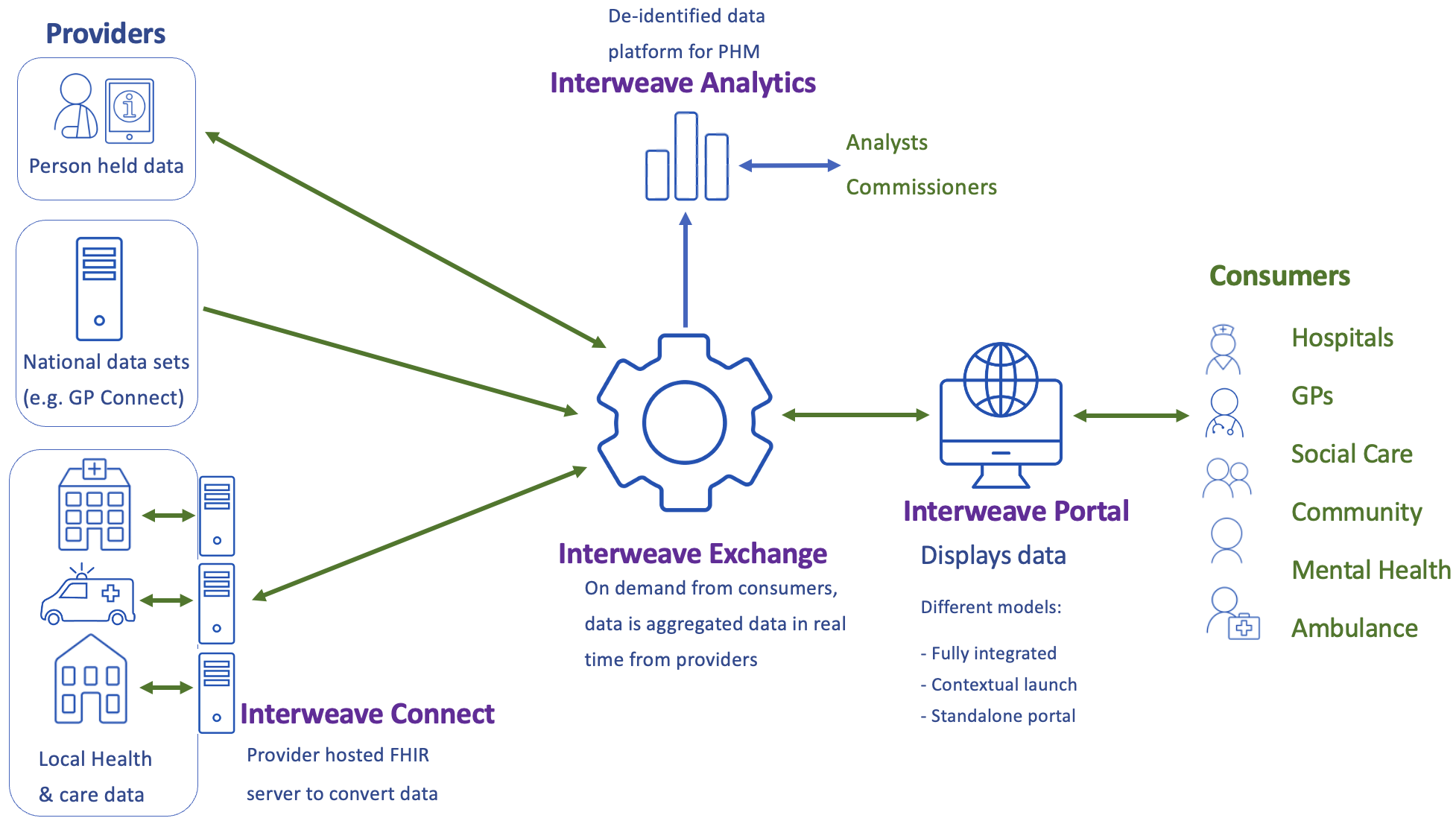
Integration Process
- Setup and Configuration:
- Define Endpoints: Specify the systems that will send and receive HL7 messages.
- Configure Message Types: Identify the types of HL7 messages to be exchanged (e.g., ADT, ORM, ORU).
- Message Flow:
- Inbound Messages: Received by the Trust Integration Engine, validated, and routed to the appropriate system.
- Outbound Messages: Generated by internal systems, processed by the TIE, and sent to external systems via Interweave Exchange.
Example Flow:
- Inbound: A patient’s lab results (HL7 ORU message) are received by the TIE from the lab system and routed to the EHR system.
- Outbound: A discharge summary (HL7 MDM message) is generated by the EHR system, processed by the TIE, and sent to the patient’s primary care provider via Interweave Exchange.
- Monitoring and Management:
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuously track the status of HL7 message exchanges.
- Error Handling: Identify and resolve issues in message processing to ensure reliable communication.
- Security and Compliance:
- Data Encryption: Protect HL7 messages during transmission.
- Access Control: Ensure only authorized systems and users can access the message data.
- Audit Trails: Maintain logs of message exchanges for regulatory compliance and auditing purposes.
Conclusion
The integration of HL7 messages via the Trust Integration Engine and Interweave Exchange is crucial for achieving seamless interoperability between healthcare systems. By adhering to standardized protocols and implementing robust security measures, these platforms ensure efficient and secure health information exchange, ultimately improving patient care and operational efficiency.